20世纪90年代,水产养殖饲料的设计没有考虑到动物可以吸收和利用的营养物质的数量
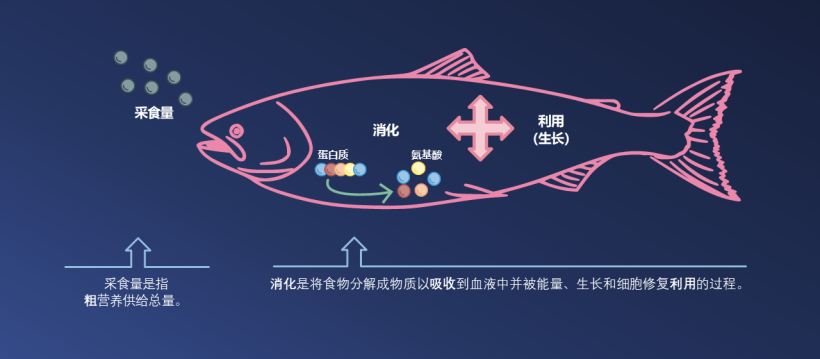
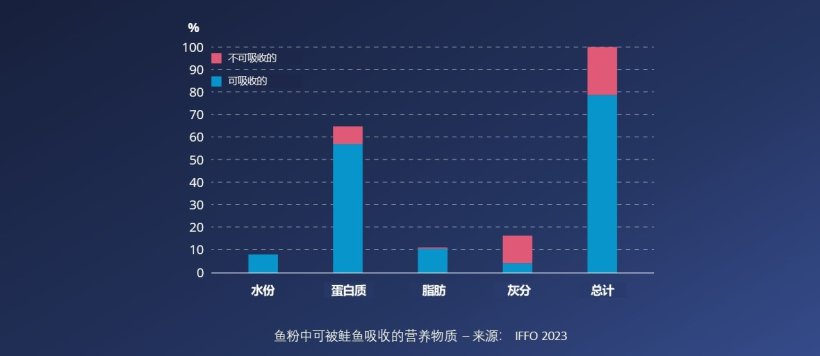
这样会导致在鲑鱼总营养供给中,本可被吸收的营养物质只有一小部分被吸收
今天,根据不同的营养和能量规格,为不同的物种和环境生产不同的饲料
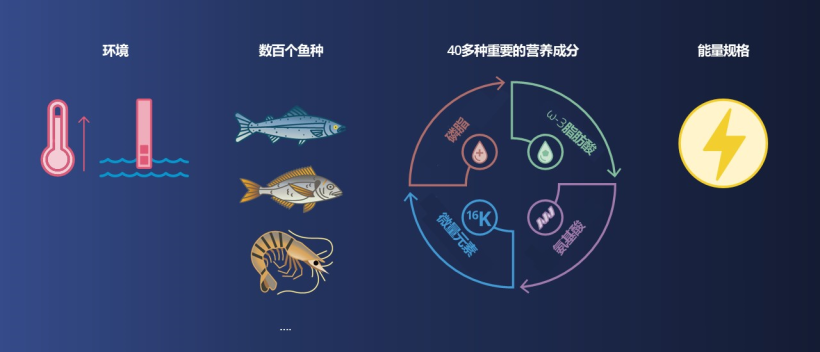
根据不同参数,饲料设计中有哪些变化?

基于精准营养的方法,海洋原料的使用更具战略性,得以发挥最大的价值…
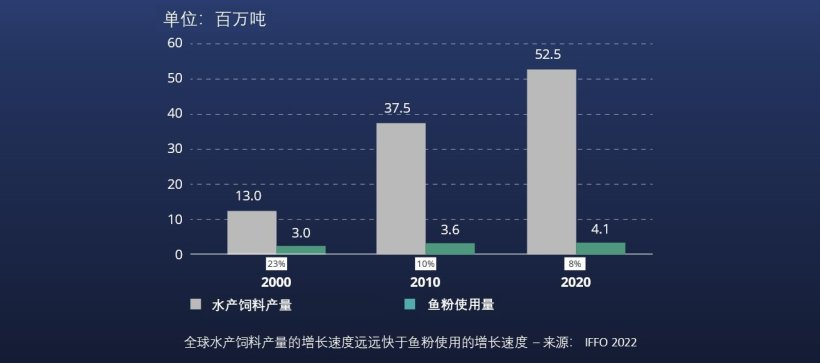
…因此提高了饲养过程的效率,也改善了给环境带来的碳足迹

因此,营养物质现在在整个生命阶段都以有针对性的方式使用。
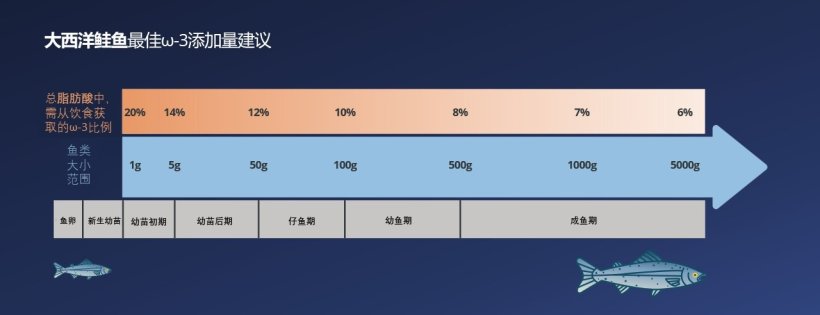
来源: Carr, I., Glencross, B., & Santigosa, E. (2023). The importance of essential fatty acids and their ratios in aquafeeds to enhance salmonid production, welfare, and human health. Frontiers in Animal Science, 4, 1147081.
Huyben, D., Grobler, T., Matthew, C., Bou, M., Ruyter, B., & Glencross, B. (2021). Requirement for omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids by Atlantic salmon is relative to the dietary lipid level. Aquaculture, 531, 735805.
Sprague, M., Xu, G., Betancor, M. B., Olsen, R. E., Torrissen, O., Glencross, B. D., & Tocher, D. R. (2019). Endogenous production of n-3 long-chain PUFA from first feeding and the influence of dietary linoleic acid and the α-linolenic: linoleic ratio in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). British Journal of Nutrition, 122(10), 1091-1102.
Glencross, B. D. (2009). Exploring the nutritional demand for essential fatty acids by aquaculture species. Reviews in Aquaculture, 1(2), 71-124.
Glencross, B. D., Tocher, D. R., Matthew, C., & Gordon Bell, J. (2014). Interactions between dietary docosahexaenoic acid and other long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids on performance and fatty acid retention in post-smolt Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Fish physiology and biochemistry, 40, 1213-1227.
Bou, M., Berge, G. M., Baeverfjord, G., Sigholt, T., Østbye, T. K., Romarheim, O. H., ... & Ruyter, B. (2017). Requirements of n-3 very long-chain PUFA in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L): effects of different dietary levels of EPA and DHA on fish performance and tissue composition and integrity. British Journal of nutrition, 117(1), 30-47.









